- Gold drops 0.67% as US limits tariffs to specific trade partners, easing global trade fears.
- Rising US Treasury yields and Dollar strength continue to sap Gold’s bullish momentum.
- Fed’s Bostic signals only one rate cut in 2025, pushing inflation target out to 2027.
Gold price extended its drop for the third consecutive trading day as sentiment improved on news that reciprocal tariffs would be focused on some United States (US) trading partners. At the time of writing, XAU/USD trades at $3,002, down 0.67%.
Wall Street trades on a positive mood, edging higher. The rise of US Treasury bond yields and broad US Dollar (USD) strength kept Bullion prices from prolonging its rally, with the yellow metal gaining over 13% in the year.
An article by Bloomberg showed that the US President Donald Trump administration would target specific countries on April 2, contrary to applying reciprocal tariffs against most countries. Instead, the measures are targeting the so-called Dirty 15 trade partners.
According to last year’s data, The Wall Street Journal reported in an article that the US has the most significant goods trade deficits with China, the EU, Mexico, Vietnam, Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, Canada, India, Thailand, Switzerland, Malaysia, Indonesia, Cambodia and South Africa.
Data-wise, S&P Global revealed that Flash PMIs for the US were mixed, with manufacturing activity contracting, while the services sector strengthened, improving from February’s figures. The divergence highlights ongoing softness in the industrial sector, mainly spurred by tariffs, amid fears of higher prices.
Recently, Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic said he supports only one rate cut this year and doesn’t see inflation returning to target until around 2027. Bostic added that inflation is expected to be very bumpy and stated that he doesn’t expect the Fed to be behind the curve.
The money market has priced in 62.5 basis points of Fed easing in 2025, according to Prime Market Terminal interest rate probabilities data.
Source: Prime Market Terminal
Daily digest market movers: Gold bears moved in, pushing prices toward $3,000
- Gold prices remain pressured by rising US Treasury yields. The US 10-year T-note yield has surged eight basis points to 4.331%.
- US real yields, as measured by the US 10-year Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities yield, which correlates inversely to Bullion prices, rise almost 2 bps to 1.980%.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the buck’s value against a basket of six currencies, rose 0.20% up to 104.35.
- The March S&P Global Manufacturing PMI showed a sharp deterioration in US factory activity, falling from 52.7 to 49.8, signaling contraction and missing expectations for a 51.7 expansion.
- In contrast, the S&P Global Services PMI surged from 51.0 to 54.3, exceeding forecasts of 50.8 and highlighting strong service sector momentum.
XAU/USD technical outlook: Gold price retreats but stays firm near $3,000
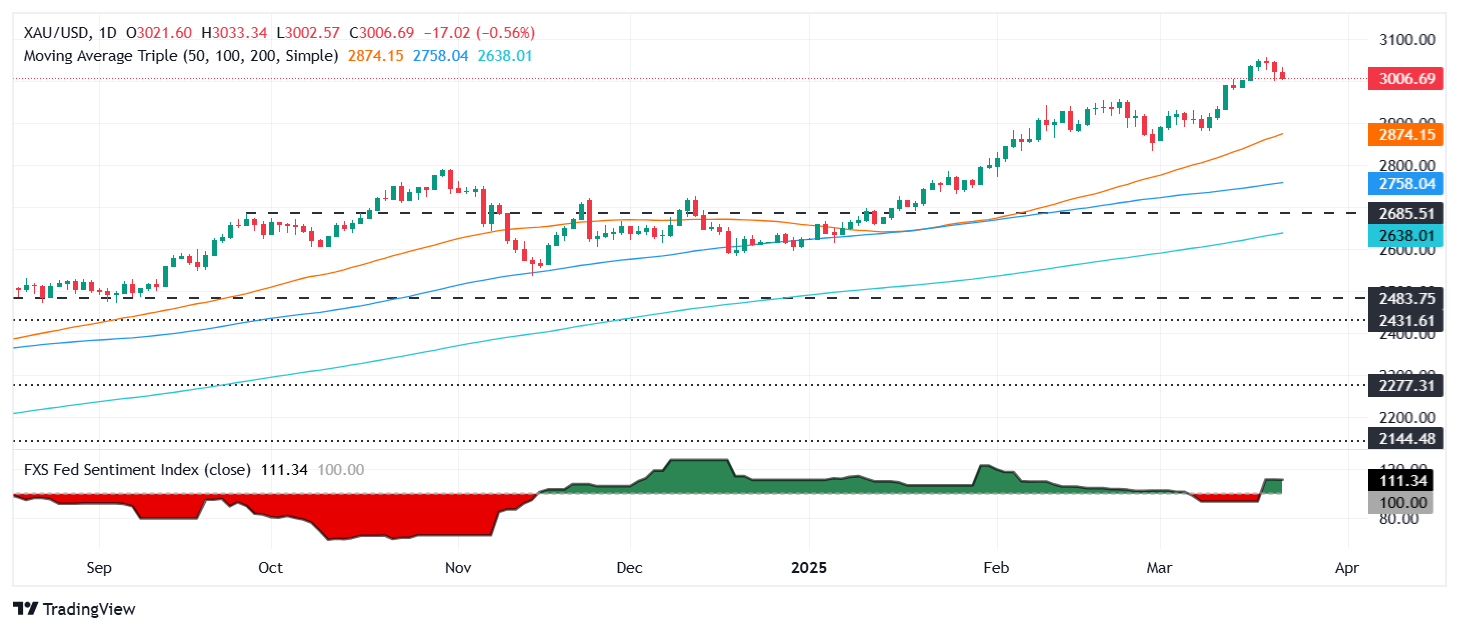
Gold price uptrend remains in place, though traders are booking profits as XAU/USD drops below $3,010, threatening to clear the $3,000 figure. A breach of the latter will expose the February 24 swing high at $2,956, followed by the $2,900 mark and the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at $2,874.
Conversely, if Bullion remains above $3,000, the first resistance would be March’s 21 peaks at $3,047, followed by the year-to-date (YTD) high at $3,057 and the $3,100 mark.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
Read the full article here
















